Research Objectives

MR can be divided up into a number of major types depending on its purpose - here are some key areas.
The phrase 'marketing research' (ie with an extra 'ing') is sometimes used as a synonym for market research, but that's not really correct. Marketing research is used to work out how best to market a product, service or company. This includes whether current marketing is working, whether a proposed new ad or approach will work and how well, what messages need to be put across to which target audiences and so on. Project types include copy testing (how good is an ad?), segmentation (how can an audience be divided up into cohesive groups), package design and testing, brand positioning (how should we be describing / portraying ourselves), and marketing mix modelling (how much time and money should we spend on which methods of marketing). Within these, copy testing can be pre-testing, post-testing, or increasingly, on-the-fly adjustments to a campaign while it is running - marketing tech allows this to be done second by second depending on what's working best. Segmentation can be working out which ages or social groups are the best targets and/or how best to approach each segment thus identified; or can be based on actual behavior - the latter can be broad brush as in traditional segments ('early adopters' vs 'technophobes' or 'impulse buyers' versus 'comparison junkies', etc..) or can now be micro-segmented down to the level of targeting individuals, usually carried out by software.
Other types of measurement research look to assess longer-term strategic objectives and performance: these include benchmarking (establishing a baseline against which to measure a company or product's future performance), customer satisfaction, brand awareness, corporate image studies and so on. Mystery shopping involves getting people to act as customers - whether by visiting a store, navigating through a web site or sampling telephone service, for example - and report on how well an organisation is performing in which areas. Audience research can be used to measure customer satisfaction or for U&A (see below) but is widely used for the distinct purpose of establishing a currency for the buying and selling of advertising - generally, the more people who watch a TV programme or read a newspaper, for example, the more the ads will sell for, and the more within a key audience segment required by an advertiser, the higher the premium.
A classic use of MR is to help identify and weigh up opportunities in new markets - whether it's market sizing (in a new country or a new sector for example, or in a different part of a sector already served - for example 'would people buy a luxury version of our currently very basic product?'). Related to this are New Product Development (NPD) and service development research, which can influence both the design and the marketing of something new, as well as whether it is launched at all.
As well as opportunities, businesses want to look at threats - competitor research includes both, and can involve a lot of searching and collection of existing data, as well as survey work to find out how competitors are perceived, for example. A huge number of companies offer solutions for tracking the social media presence of clients and their competitors, with analysis of their relative perceived strengths and weaknesses, as well as alerts when specific events threaten to damage a brand or open up new opportunities.
Increasingly, businesses carry out research with the general aim of better understanding the behaviour and needs of their customers, users or audience, feeding this into various functions including sales, operations, NPD and customer service. Some such studies are called Usage and Attitude research (U&A).
Other kinds of research involve collecting data within a company - interviewing staff for example - or assessing internal systems and distribution channels to look for efficiencies; or talking to voters or citizens about political choices and social trends. Employee research and social / opinion research are sometimes lumped in with market research and sometimes dealt with separately - but we include them in our coverage.
The above is just intended as an introduction to the ways in which we divide up types of research - there are a lot of alternative ways to divide it, and some other categories which might be added, but we think we've covered most MR activity in the above.
As you can see even from this, there's lots of overlap and precise categorisation of many studies is impossible. Nevertheless MR organisations like to try, and produce interesting stats on which types of research are conducted where - here's ESOMAR's breakdown of research types at the global level in 2015:
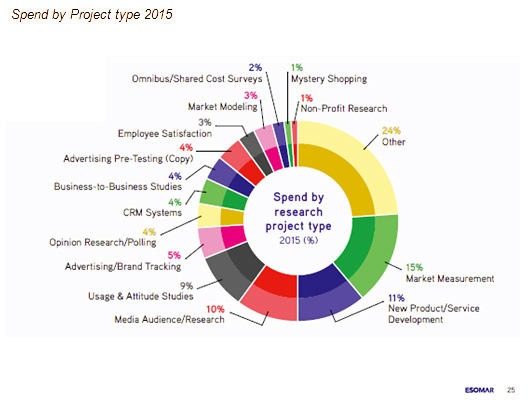
Industry sectors
MR is spread across the whole gamut of industries, market sectors or 'verticals' as those in the trade sometimes call them. Certain sectors are very important and quite distinct and a research professional can specialise in them all his or her career - on MrWeb we actually separate out pharmaceutical / healthcare sector jobs if people want to search that way, just because we've had a lot more requests to do so, over the years, than for any other sector. And indeed, it's a key sector worldwide - see below - and particularly in the US where it takes a whopping 19% of all budgets. We're not surprised to see media, public sector, financial services and automotive also in their top 6 along with the 'consumer' category which frankly is more difficult to define. Retail, consumer, shopper and FMCG are expressions which are sometimes confused, sometimes combined, but obviously consumer goods are a huge part of the economy however you look at it.
Global spend by client type:
Source: ESOMAR Global MR report 2016
| Consumer non-durables | 23% } |
| Consumer Durables | 4% } these 2 were previously combined as 'manufacturing' |
| Media & Entertainment | 15% |
| Pharma | 13% |
| Govt and non-profit | 8% |
| Financial Services | 7% |
| Automotive | 6% |
| Telecoms & ICT | 5% |
| Wholesale and Retail inc.oil | 5% |
| Research Institutes | 3% |
| Ad agencies | 2% |
| Utilities | 1% |
| Other | 8% |
| includes food, beverages and confectionery 12%; then OTC medicines, cosmetics & hygeine; then tobacco & cigarette are smallest sub-sector. | |
| 21% in North America | |
* includes food, beverages and confectionery 12%; then OTC medicines, cosmetics & hygeine; then tobacco & cigarette are smallest sub-sector.** 21% in North America
Next, we'll look at how this is done, although that's so varied and fast-changing, we'll look at the traditional route first to get our bearings:
About the industry - contents...
1. What is MR and how is it changing?
A comprehensive guide to what we do, how it's changing, and who else does similar stuff.
2. The global industry today
The supply side: revenues, rankings and company info, full listings.
3. Careers in MR
An introduction to the career ladder, activities, salaries and choices.